6.6 Border Lines
1.McMahon Line
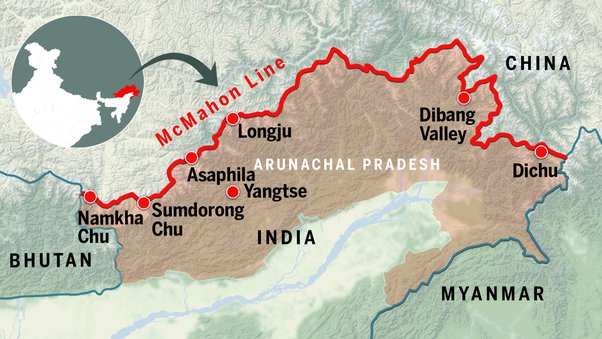
The McMahon Line is a demarcation line is a boundary line between India and China drawn on map referred to in the Simla Convention, a treaty between Britain and Tibet signed in 1914.
Although its legal status is disputed, it is currently the effective boundary between China and India.
This dispute was used a pretext in a war between China and India in 1962
It gets its name from Sir Henry McMahon who was the Foreign Secretary of the British Colonial Government of India.
McMahon Line is a boundary line between India and China which was determined after the Shimla Convention was signed on 3rd July 1949. • This boundary is around 90 km and extends from Bhutan in the west to around 260 km in the east reaching the Brahmaputra river.
While the line of actual control is a line of demarcation between India and China and is located in the Western borders of both these countries that is between the Ladakh region of India and China.
2.Durand Line
The Durand Line is the international 2,430-kilometre (1,510 mi) land border between Afghanistan and Pakistan in South-Central Asia. It was established after an 1897 memorandum of understanding (MoU) between Mortimer Durand of British India and Afghan Amir Abdur Rahman Khan. Referred to as a frontier line, it is named after Mortimer Durand, who was the Foreign Secretary of colonial British India at the time
Radcliffe Line
Boundary Commission, consultative committee created in July 1947 to recommend how the Punjab and Bengal regions of the Indian subcontinent were to be divided between India and Pakistan shortly before each was to become independent from Britain. The commission—appointed by Lord Mountbatten, the final viceroy of British India—consisted of four members from the Indian National Congress and four from the Muslim League and was chaired by Sir Cyril Radcliffe
The Radcliffe Line became the international border between India and Pakistan (which also included what is now Bangladesh) during the partition of India. The line divided Bengal into Indian held West Bengal and East Bengal which became East Pakistan in 1956. The line was decided by the Border Commissions headed by Sir Cyril Radcliffe, who was to divide equitably 175,000 square miles of territory with 88 million people. The line took effect on 17 August 1947 after the Partition of India.
